HSE Neurolinguists Reveal What Makes Apps Effective for Aphasia Rehabilitation
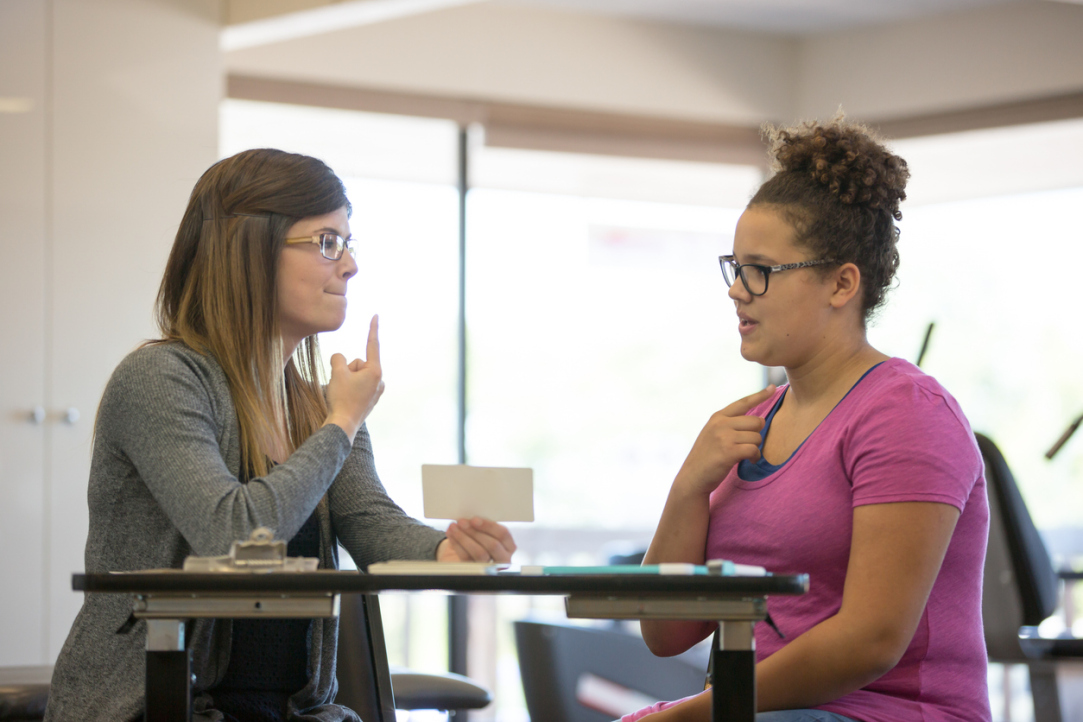

Scientists at the HSE Centre for Language and Brain have identified key factors that increase the effectiveness of mobile and computer-based applications for aphasia rehabilitation. These key factors include automated feedback, a variety of tasks within the application, extended treatment duration, and ongoing interaction between the user and the clinician. The article has been published in NeuroRehabilitation.
Aphasia is a disorder characterised by complete or partial loss of the ability to speak and understand speech, caused by damage to areas of the brain responsible for language functions. The primary causes of aphasia include stroke, traumatic brain injury, inflammatory brain diseases, brain tumours, and dementia.
Aphasia significantly reduces a person's quality of life, prompting scientists to search for effective ways to restore the language functions impaired by the condition. With the widespread use of smartphones and tablets, a promising and rapidly evolving area of rehabilitation has emerged: serious games (SG) integrated into applications.
These are a special type of digital game designed not only for entertainment, but also to serve specific educational, training, or research purposes. In education, they support professional training, student learning, and foreign language acquisition. In healthcare, such games are used for patient rehabilitation.
Using a specially designed application, a person with aphasia can complete language training tasks and gradually recover their lost abilities. The effectiveness of such applications has already been demonstrated, but it remained unclear which specific tasks and features should be included, and how long users should engage with them to achieve optimal results.
Scientists from the HSE Centre for Language and Brain searched the PubMed and ScienceDirect databases and selected 18 studies which tested mobile and computer applications for aphasia rehabilitation.
The researchers focused specifically on cases where using an application produced remarkable results. For example, a patient who practiced naming 100 words improved to naming 150 words or was able to use the learned words not only in speech but also in writing. Sometimes, using serious games led to the development of related skills; for example, while training language functions, a person’s attention also improved.
In 14 of the 18 papers analysed (78%), patient use of the application resulted in positive effects. While most studies confirmed the effectiveness of the applications based on primary outcomes—ie improvement in the specific skills being trained—eight articles (44%) reported results that exceeded expectations, often showing that patients could apply the trained words in other contexts, such as writing. Additionally, two studies reported improvements in other higher cognitive functions.
The analysis revealed that the effectiveness of the applications was influenced by factors such as automated feedback, a diverse range of training tasks, extended treatment duration, and interaction between the patient and clinician. The latter is particularly important, as clinicians provide additional motivation and assess interim progress.
'At our centre, we are developing a game for aphasia rehabilitation. Reviewing existing studies will help us optimise its testing and incorporate the essential features needed for effective use. Many existing applications include few gamification elements and function more like digital workbooks with exercises. We aim to address this limitation to increase user engagement,' explains Georgii Gorshkov, Junior Research Fellow at the HSE Centre for Language and Brain.
The study was conducted with support from the Government of Moscow (Grant No. 1403-18/23).
See also:
Scientists Discover Why Parents May Favour One Child Over Another
An international team that included Prof. Marina Butovskaya from HSE University studied how willing parents are to care for a child depending on the child’s resemblance to them. The researchers found that similarity to the mother or father affects the level of care provided by parents and grandparents differently. Moreover, this relationship varies across Russia, Brazil, and the United States, reflecting deep cultural differences in family structures in these countries. The study's findings have been published in Social Evolution & History.
When a Virus Steps on a Mine: Ancient Mechanism of Infected Cell Self-Destruction Discovered
When a virus enters a cell, it disrupts the cell’s normal functions. It was previously believed that the cell's protective response to the virus triggered cellular self-destruction. However, a study involving bioinformatics researchers at HSE University has revealed a different mechanism: the cell does not react to the virus itself but to its own transcripts, which become abnormally long. The study has been published in Nature.
Researchers Identify Link between Bilingualism and Cognitive Efficiency
An international team of researchers, including scholars from HSE University, has discovered that knowledge of a foreign language can improve memory performance and increase automaticity when solving complex tasks. The higher a person’s language proficiency, the stronger the effect. The results have been published in the journal Brain and Cognition.
Artificial Intelligence Transforms Employment in Russian Companies
Russian enterprises rank among the world’s top ten leaders in AI adoption. In 2023, nearly one-third of domestic companies reported using artificial intelligence. According to a new study by Larisa Smirnykh, Professor at the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences, the impact of digitalisation on employment is uneven: while the introduction of AI in small and large enterprises led to a reduction in the number of employees, in medium-sized companies, on the contrary, it contributed to job growth. The article has been published in Voprosy Ekonomiki.
Lost Signal: How Solar Activity Silenced Earth's Radiation
Researchers from HSE University and the Space Research Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences analysed seven years of data from the ERG (Arase) satellite and, for the first time, provided a detailed description of a new type of radio emission from near-Earth space—the hectometric continuum, first discovered in 2017. The researchers found that this radiation appears a few hours after sunset and disappears one to three hours after sunrise. It was most frequently observed during the summer months and less often in spring and autumn. However, by mid-2022, when the Sun entered a phase of increased activity, the radiation had completely vanished—though the scientists believe the signal may reappear in the future. The study has been published in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics.
Banking Crises Drive Biodiversity Loss
Economists from HSE University, MGIMO University, and Bocconi University have found that financial crises have a significant negative impact on biodiversity and the environment. This relationship appears to be bi-directional: as global biodiversity declines, the likelihood of new crises increases. The study examines the status of populations encompassing thousands of species worldwide over the past 50 years. The article has been published in Economics Letters, an international journal.
Scientists Discover That the Brain Responds to Others’ Actions as if They Were Its Own
When we watch someone move their finger, our brain doesn’t remain passive. Research conducted by scientists from HSE University and Lausanne University Hospital shows that observing movement activates the motor cortex as if we were performing the action ourselves—while simultaneously ‘silencing’ unnecessary muscles. The findings were published in Scientific Reports.
Russian Scientists Investigate Age-Related Differences in Brain Damage Volume Following Childhood Stroke
A team of Russian scientists and clinicians, including Sofya Kulikova from HSE University in Perm, compared the extent and characteristics of brain damage in children who experienced a stroke either within the first four weeks of life or before the age of two. The researchers found that the younger the child, the more extensive the brain damage—particularly in the frontal and parietal lobes, which are responsible for movement, language, and thinking. The study, published in Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology, provides insights into how age can influence the nature and extent of brain lesions and lays the groundwork for developing personalised rehabilitation programmes for children who experience a stroke early in life.
Scientists Test Asymmetry Between Matter and Antimatter
An international team, including scientists from HSE University, has collected and analysed data from dozens of experiments on charm mixing—the process in which an unstable charm meson oscillates between its particle and antiparticle states. These oscillations were observed only four times per thousand decays, fully consistent with the predictions of the Standard Model. This indicates that no signs of new physics have yet been detected in these processes, and if unknown particles do exist, they are likely too heavy to be observed with current equipment. The paper has been published in Physical Review D.
HSE Scientists Reveal What Drives Public Trust in Science
Researchers at HSE ISSEK have analysed the level of trust in scientific knowledge in Russian society and the factors shaping attitudes and perceptions. It was found that trust in science depends more on everyday experience, social expectations, and the perceived promises of science than on objective knowledge. The article has been published in Universe of Russia.