Russian Scientists Integrate Microdisk Laser and Waveguide on a Single Substrate
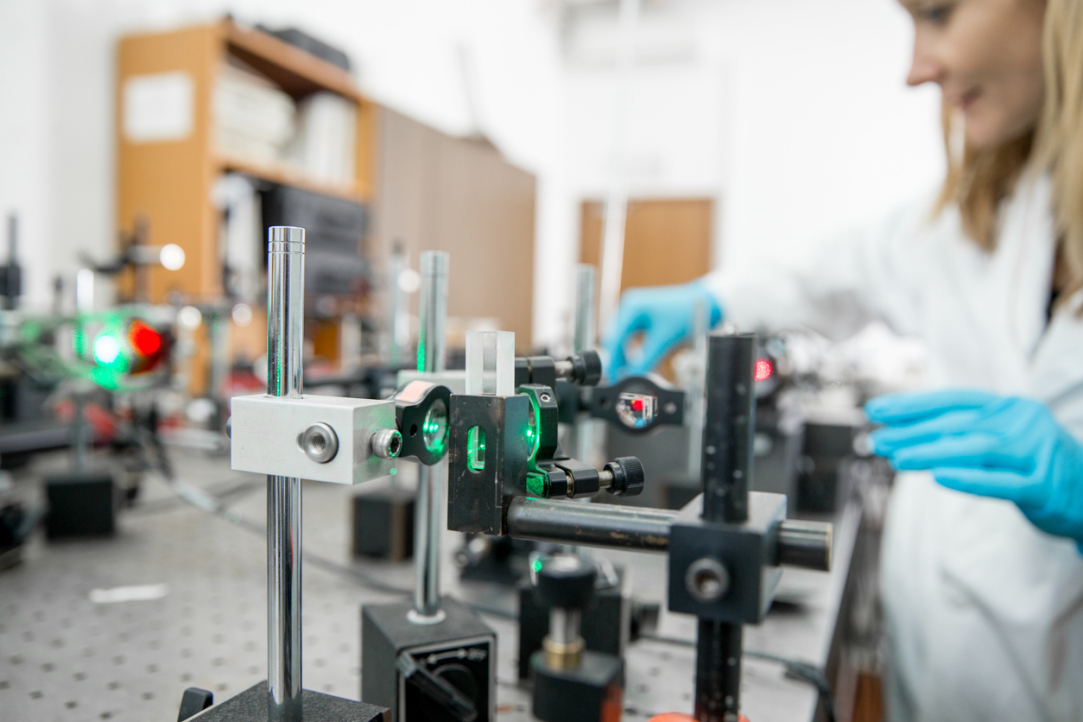
A group of Russian scientists led by Professor Natalia Kryzhanovskaya at HSE Campus in St Petersburg has been researching microdisk lasers with an active region based on arsenide quantum dots. For the first time, researchers have successfully developed a microdisk laser coupled with an optical waveguide and a photodetector on a single substrate. This design enables the implementation of a basic photonic circuit on the same substrate as the radiation source (microlaser). In the future, this will help speed up data transfer and reduce equipment weight without compromising quality. The study results have been published in Semiconductors.
The growing demands for higher speed and larger volumes of transmitted information necessitate improvements to current communication methods. Photonic integrated circuits (PICs), which use light to transmit information, operate faster, generate less heat, are more resistant to interference, and consume less energy compared to their electronic counterparts.
However, their effective use requires efficient, compact light sources, such as gallium arsenide (GaAs) microdisk lasers. The length of a conventional Fabry–Perot laser is around 1 mm, while a microdisk laser can be up to 1,000 times smaller. In this study, the laser size was reduced to a diameter of 30 to 40 microns.
Effective directional radiation output is essential for the successful implementation of optical communication in photonic integrated circuits (PICs). Directional radiation can be achieved by optically coupling microlasers with a nearby waveguide. The authors of the paper designed and fabricated both a microlaser and a waveguide from a single epitaxial structure, resulting in reduced size and increased stability.
'Creating microdisk lasers coupled to a waveguide is a challenging task. This process involves developing a thin-film epitaxial structure with a specific composition. In our case, we employed gas-phase epitaxy of metal-organic compounds, a method for layered formation of crystals of different substances on top of one another. Lasers and waveguides were created from the resulting structure. This was made possible thanks to the innovations developed by the Mokerov Institute of Ultra High Frequency Semiconductor Electronics of the Russian Academy of Sciences. All these processes required the use of advanced technology and the efforts of a team of experienced, talented, and qualified specialists,' according to Nikita Fominykh, Junior Research Fellow of the International Laboratory of Quantum Optoelectronics at HSE Campus in St Petersburg.
In addition to radiation sources, radiation receivers are also essential for the operation of PICs. In this work, waveguide photodetectors fulfil this role. Thus, it becomes possible to create an optocoupler that combines a microlaser and a waveguide photodetector with a matching operating wavelength on a single substrate. The photodetector used in the optocoupler measured no more than 90 microns, enabling the creation of a highly compact and energy-efficient optocoupler.
'Microdisk lasers are unique optoelectronic devices. With a size comparable to the diameter of a spider silk thread, they can generate a significant amount of optical power. We have experimentally demonstrated that all optoelectronic components necessary for a photonic integrated circuit—a microdisk laser, a waveguide, and a photodetector—can be fabricated from a single epitaxial heterostructure on the same substrate,' says co-author of the paper Natalia Kryzhanovskaya, Head of the International Laboratory of Quantum Optoelectronics at HSE Campus in St Petersburg.
See also:
Larger Groups of Students Use AI More Effectively in Learning
Researchers at the Institute of Education and the Faculty of Economic Sciences at HSE University have studied what factors determine the success of student group projects when they are completed with the help of artificial intelligence (AI). Their findings suggest that, in addition to the knowledge level of the team members, the size of the group also plays a significant role—the larger it is, the more efficient the process becomes. The study was published in Innovations in Education and Teaching International.
New Models for Studying Diseases: From Petri Dishes to Organs-on-a-Chip
Biologists from HSE University, in collaboration with researchers from the Kulakov National Medical Research Centre for Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Perinatology, have used advanced microfluidic technologies to study preeclampsia—one of the most dangerous pregnancy complications, posing serious risks to the life and health of both mother and child. In a paper published in BioChip Journal, the researchers review modern cellular models—including advanced placenta-on-a-chip technologies—that offer deeper insights into the mechanisms of the disorder and support the development of effective treatments.
Using Two Cryptocurrencies Enhances Volatility Forecasting
Researchers from the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences have found that Bitcoin price volatility can be effectively predicted using Ethereum, the second-most popular cryptocurrency. Incorporating Ethereum into a predictive model reduces the forecast error to 23%, outperforming neural networks and other complex algorithms. The article has been published in Applied Econometrics.
Administrative Staff Are Crucial to University Efficiency—But Only in Teaching-Oriented Institutions
An international team of researchers, including scholars from HSE University, has analysed how the number of non-academic staff affects a university’s performance. The study found that the outcome depends on the institution’s profile: in research universities, the share of administrative and support staff has no effect on efficiency, whereas in teaching-oriented universities, there is a positive correlation. The findings have been published in Applied Economics.
Physicists at HSE University Reveal How Vortices Behave in Two-Dimensional Turbulence
Researchers from the Landau Institute for Theoretical Physics of the Russian Academy of Sciences and the HSE University's Faculty of Physics have discovered how external forces affect the behaviour of turbulent flows. The scientists showed that even a small external torque can stabilise the system and extend the lifetime of large vortices. These findings may improve the accuracy of models of atmospheric and oceanic circulation. The paper has been published in Physics of Fluids.
Solvent Instead of Toxic Reagents: Chemists Develop Environmentally Friendly Method for Synthesising Aniline Derivatives
An international team of researchers, including chemists from HSE University and the A.N. Nesmeyanov Institute of Organoelement Compounds of the Russian Academy of Sciences (INEOS RAS), has developed a new method for synthesising aniline derivatives—compounds widely used in the production of medicines, dyes, and electronic materials. Instead of relying on toxic and expensive reagents, they proposed using tetrahydrofuran, which can be derived from renewable raw materials. The reaction was carried out in the presence of readily available cobalt salts and syngas. This approach reduces hazardous waste and simplifies the production process, making it more environmentally friendly. The study has been published in ChemSusChem.
How Colour Affects Pricing: Why Art Collectors Pay More for Blue
Economists from HSE University, St Petersburg State University, and the University of Florida have found which colours in abstract paintings increase their market value. An analysis of thousands of canvases sold at auctions revealed that buyers place a higher value on blue and favour bright, saturated palettes, while showing less appreciation for traditional colour schemes. The article has been published in Information Systems Frontiers.
New Method for Describing Graphene Simplifies Analysis of Nanomaterials
An international team, including scientists from HSE University, has proposed a new mathematical method to analyse the structure of graphene. The scientists demonstrated that the characteristics of a graphene lattice can be represented using a three-step random walk model of a particle. This approach allows the lattice to be described more quickly and without cumbersome calculations. The study has been published in Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and Theoretical.
Scientists Have Modelled Supercapacitor Operation at Molecular and Ionic Level
HSE scientists used supercomputer simulations to study the behaviour of ions and water molecules inside the nanopores of a supercapacitor. The results showed that even a very small amount of water alters the charge distribution inside the nanopores and influences the device’s energy storage capacity. This approach makes it possible to predict how supercapacitors behave under different electrolyte compositions and humidity conditions. The paper has been published in Electrochimica Acta. The study was supported by a grant from the Russian Science Foundation (RSF).
Designing an Accurate Reading Skills Test: Why Parallel Texts are Important in Dyslexia Diagnosis
Researchers from the HSE Centre for Language and Brain have developed a tool for accurately assessing reading skills in adults with reading impairments. It can be used, for instance, before and after sessions with a language therapist. The tool includes two texts that differ in content but are equal in complexity: participants were observed to read them at the same speed, make a similar number of errors, and understand the content to the same degree. Such parallel texts will enable more accurate diagnosis of dyslexia and better monitoring of the effectiveness of interventions aimed at addressing it. The paper has been published in Educational Studies.