Russian Scientists Develop New Compound for Treating Aggressive Tumours

A team of Russian researchers has synthesised a novel compound for boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT), a treatment for advanced cancer that uses the boron-10 isotope. The compound exhibits low toxicity, excellent water solubility, and eliminates the need for administering large volumes. Most importantly, the active substance reaches the tumour with minimal impact on healthy tissues. The study was published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences shortly before World Cancer Day, observed annually on February 4.
Boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) is an advanced cancer treatment that leverages the properties of the boron-10 isotope. The method involves first saturating tumour cells with boron-10, followed by irradiation with thermal neutrons. This triggers a nuclear reaction that selectively destroys cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue. Thus, the treatment success largely depends on the compound's ability to effectively deliver boron-10 to the tumour and maintain the necessary boron concentration.
A team of scientists from the HSE Faculty of Chemistry, the Institute of General and Inorganic Chemistry of the Russian Academy of Sciences, and the N.N. Blokhin National Medical Research Centre of Oncology has developed three compounds that combine the closo-dodecaborate anion with amino acids containing a side-chain amino group. The molecules are structurally similar to natural amino acids, allowing them to 'trick' the body's transport systems into capturing and delivering them to cells, including cancer cells. This makes the substance effective at targeting tumours, where it accumulates.
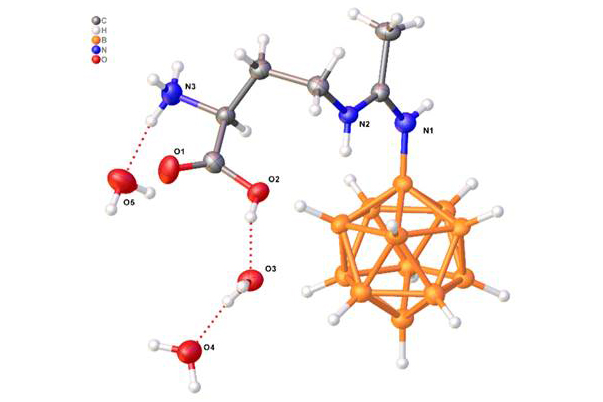
One of the compounds demonstrated low toxicity, with the half-lethal dose (LD50) for experimental animals ranging from 150 to 300 mg per kilogram of body weight. In experiments, the compound not only demonstrated the ability to accumulate boron in tumour tissues but also confirmed its effectiveness in animals. When administered to laboratory mice, the boron concentration in melanoma tumour cells was six times higher than in healthy tissues after 45 minutes.
The compound can exist in two forms depending on the pH level. The first form is a sodium salt, which is highly soluble in water under conditions close to physiological pH, making it convenient for therapeutic use. The second form occurs upon acidification, when the compound transforms into an insoluble internal salt useful for obtaining a medically pure product during the stages of synthesis, isolation, and purification.

Margarita Ryabchikova
'The aim of the study was to reduce toxicity and simplify the compound purification process, building on data from previous research. As a result, three new compounds were synthesised. One of them exhibited optimal characteristics: it does not cause significant side effects when administered intravenously and dissolves well in water, setting it apart from existing therapeutic drugs,' explains study author Margarita Ryabchikova, a third-year student at the HSE Faculty of Chemistry. 'We aimed not only for high efficacy but also for production convenience. The developed method can be easily scaled to produce the required quantities of the product while remaining economically viable.'
The study demonstrated that the new compound accumulates more effectively in the tissues of certain types of tumours compared to the currently used drug. This is an important step toward developing a safer and more accessible therapy. The research is still in its early stages, but this development has the potential to significantly improve cancer treatment outcomes and broaden the applications of boron neutron capture therapy in the fight against various types of tumours.
See also:
Scientists Have Modelled Supercapacitor Operation at Molecular and Ionic Level
HSE scientists used supercomputer simulations to study the behaviour of ions and water molecules inside the nanopores of a supercapacitor. The results showed that even a very small amount of water alters the charge distribution inside the nanopores and influences the device’s energy storage capacity. This approach makes it possible to predict how supercapacitors behave under different electrolyte compositions and humidity conditions. The paper has been published in Electrochimica Acta. The study was supported by a grant from the Russian Science Foundation (RSF).
Designing an Accurate Reading Skills Test: Why Parallel Texts are Important in Dyslexia Diagnosis
Researchers from the HSE Centre for Language and Brain have developed a tool for accurately assessing reading skills in adults with reading impairments. It can be used, for instance, before and after sessions with a language therapist. The tool includes two texts that differ in content but are equal in complexity: participants were observed to read them at the same speed, make a similar number of errors, and understand the content to the same degree. Such parallel texts will enable more accurate diagnosis of dyslexia and better monitoring of the effectiveness of interventions aimed at addressing it. The paper has been published in Educational Studies.
Internal Clock: How Heart Rate and Emotions Shape Our Perception of Time
Our perception of time depends on heart rate—this is the conclusion reached by neuroscientists at HSE University. In their experiment, volunteers watched short videos designed to evoke specific emotions and estimated each video's duration, while researchers recorded their heart activity using ECG. The study found that the slower a participant's heart rate, the shorter they perceived the video to be—especially when watching unpleasant content. The study has been published in Frontiers in Psychology.
Scientists Identify Personality Traits That Help Schoolchildren Succeed Academically
Economists from HSE University and the Southern Federal University have found that personality traits such as conscientiousness and open-mindedness help schoolchildren improve their academic performance. The study, conducted across seven countries, was the first large-scale international analysis of the impact of character traits on the academic achievement of 10 and 15-year-olds. The findings have been published in the International Journal of Educational Research.
HSE Scientists Reveal How Disrupted Brain Connectivity Affects Cognitive and Social Behaviour in Children with Autism
An international team of scientists, including researchers from the HSE Centre for Language and Brain, has for the first time studied the connectivity between the brain's sensorimotor and cognitive control networks in children with autism. Using fMRI data, the researchers found that connections within the cognitive control network (responsible for attention and inhibitory control) are weakened, while connections between this network and the sensorimotor network (responsible for movement and sensory processing) are, by contrast, excessively strong. These features manifest as difficulties in social interaction and behavioural regulation in children. The study has been published in Brain Imaging and Behavior.
Similar Comprehension, Different Reading: How Native Language Affects Reading in English as a Second Language
Researchers from the MECO international project, including experts from the HSE Centre for Language and Brain, have developed a tool for analysing data on English text reading by native speakers of more than 19 languages. In a large-scale experiment involving over 1,200 people, researchers recorded participants’ eye movements as they silently read the same English texts and then assessed their level of comprehension. The results showed that even when comprehension levels were the same, the reading process—such as gaze fixations, rereading, and word skipping—varied depending on the reader's native language and their English proficiency. The study has been published in Studies in Second Language Acquisition.
Mortgage and Demography: HSE Scientists Reveal How Mortgage Debt Shapes Family Priorities
Having a mortgage increases the likelihood that a Russian family will plan to have a child within the next three years by 39 percentage points. This is the conclusion of a study by Prof. Elena Vakulenko and doctoral student Rufina Evgrafova from the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences. The authors emphasise that this effect is most pronounced among women, people under 36, and those without children. The study findings have been published in Voprosy Ekonomiki.
Scientists Discover How Correlated Disorder Boosts Superconductivity
Superconductivity is a unique state of matter in which electric current flows without any energy loss. In materials with defects, it typically emerges at very low temperatures and develops in several stages. An international team of scientists, including physicists from HSE MIEM, has demonstrated that when defects within a material are arranged in a specific pattern rather than randomly, superconductivity can occur at a higher temperature and extend throughout the entire material. This discovery could help develop superconductors that operate without the need for extreme cooling. The study has been published in Physical Review B.
Scientists Develop New Method to Detect Motor Disorders Using 3D Objects
Researchers at HSE University have developed a new methodological approach to studying motor planning and execution. By using 3D-printed objects and an infrared tracking system, they demonstrated that the brain initiates the planning process even before movement begins. This approach may eventually aid in the assessment and treatment of patients with neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s. The paper has been published in Frontiers in Human Neuroscience.
Civic Identity Helps Russians Maintain Mental Health During Sanctions
Researchers at HSE University have found that identifying with one’s country can support psychological coping during difficult times, particularly when individuals reframe the situation or draw on spiritual and cultural values. Reframing in particular can help alleviate symptoms of depression. The study has been published in Journal of Community Psychology.